The Dangers of an Underactive Thyroid (Hypothyroidism)
The Hidden Threat: Recognize and Address the Symptoms
Are you feeling unusually tired, struggling with unexplained weight gain, or experiencing persistent cold sensitivity? These could be signs of an underactive thyroid or hypothyroidism, a condition that affects millions worldwide but often goes undiagnosed. Understanding the symptoms and dangers of hypothyroidism is crucial for maintaining your health and well-being.
Understanding the Thyroid
The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland in the front of the neck that produces hormones. It is part of the endocrine system and produces stores, and circulates hormones throughout the bloodstream. Many of these hormones affect cell production. The thyroid produces two main hormones: triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). The output of these two hormones is monitored and controlled by two glands in the brain: the hypothalamus and the pituitary. The pituitary gland releases thyroid-stimulating hormones (TSH) to regulate the thyroid gland’s activity. The hormones produced by the thyroid gland regulate many bodily functions:
- Metabolism: The process of turning food into energy
- Heart rate: Can be rapid or irregular
- Weight: Can be unintentional loss or gain
- Moods: Can cause anxiety, nervousness, or jitters
- Breathing: Can cause shortness of breath with little exertion
- Muscle weakness: Can be noticeable in the forearms or thighs
Hormonal Imbalances
Hormonal imbalances involving the thyroid can significantly impact overall health. These imbalances can be caused by various factors, including:
- Iodine deficiency: The most common cause of thyroid disease, iodine deficiency can lead to hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid). When the body lacks sufficient iodine, the thyroid gland enlarges to capture more iodine, resulting in goiter.
- Autoimmune diseases: Hashimoto’s disease is the most common cause of hypothyroidism. Autoimmune diseases occur when the immune system creates antibodies that attack healthy tissues, including the thyroid gland.
- Stress: Prolonged stress can lead to hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid).
- Upper respiratory infections: Infections that damage thyroid cells can cause De Quervain thyroiditis, also known as subacute granulomatous thyroiditis.
- Pharmaceutical drugs: Certain medications can affect thyroid function by interfering with hormone production, binding, activation, or metabolism. For example, lithium, used to treat psychiatric conditions, can impact thyroid function.
- Thyroiditis: Inflammation of the thyroid gland due to infection, autoimmune disorder, or other medical conditions can cause a temporary spike in thyroid activity (hyperthyroidism) followed by underactivity.
- Radiation treatment: Radiation used to treat head and neck cancers can damage the thyroid gland, leading to hypothyroidism.
What Causes an Underactive Thyroid (Hypothyroidism)?
Hypothyroidism, or an underactive thyroid, occurs when the thyroid does not produce enough thyroid hormones. According to the Mayo Clinic, hypothyroidism may not cause noticeable symptoms initially but can lead to severe health issues if left untreated.
Symptoms of Hypothyroidism
- Fatigue: Persistent tiredness even after adequate sleep.
- Cold sensitivity: Feeling cold when others are comfortable.
- Dry skin: Slowed skin cell turnover, leading to dryness.
- Unexplained weight gain: Weight gain of 5-10 pounds, usually due to water and salt retention.
- Constipation: Reduced motor activity in the esophagus and stomach.
- Changes in the menstrual cycle: Heavier or irregular periods.
How Hypothyroidism Is Diagnosed
Blood tests are used to diagnose hypothyroidism; however, it can be challenging to recognize the condition initially, as symptoms often resemble those of other conditions. If you have symptoms of hypothyroidism, your healthcare provider may order a thyroid function test, which measures TSH and T4 levels in your blood. A high TSH level and a low T4 level usually indicate hypothyroidism. Additional tests for thyroid antibodies may also be conducted to check for Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
The Dangers of Untreated Hypothyroidism
Untreated hypothyroidism can lead to several health issues, including:
- Goiter: Enlargement of the thyroid gland, causing swallowing or breathing difficulties.
- Peripheral neuropathy: Damage to peripheral nerves, causing pain, numbness, and tingling in the arms and legs.
- Heart problems: High levels of LDL (bad) cholesterol, increasing the risk of heart disease.
- Infertility: Low thyroid hormone levels can interfere with ovulation.
- Birth defects: Babies born to mothers with untreated thyroid disease may have a higher risk of congenital disabilities.
- Myxedema coma: A rare, life-threatening condition caused by long-term untreated hypothyroidism, characterized by intense cold intolerance, drowsiness, and extreme lack of energy, leading to unconsciousness. Myxedema coma is a medical emergency that requires immediate attention, as it has a high mortality rate.
It is important to seek timely treatment to prevent further health issues. Let’s examine the available treatment options.
Medical Treatment for Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism is typically treated with daily hormone replacement tablets known as levothyroxine. Levothyroxine replaces the thyroxine hormone when your thyroid does not produce enough. Adjusting the dosage is crucial, and regular blood tests are necessary to ensure the correct hormone levels are maintained.
In addition to levothyroxine, some patients may benefit from:
- Liothyronine (T3): Sometimes prescribed along with levothyroxine for better symptom control.
- Dietary changes: Incorporating a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients.
- Regular exercise: Helps improve overall well-being and metabolic function
Natural Remedies to Combat Hypothyroidism
Please note that the following information does not replace medical advice or prescribed medications.
While your provider may prescribe thyroid medication, these medications have side effects; therefore, natural remedies (supplements) may be a better option or—at the very least—complement medical treatment by addressing the root causes of hypothyroidism. Common natural remedies include:
- Selenium: Essential for thyroid hormone metabolism. Dr. Joel Wallach, a naturopathic physician and author of “Dead Doctors Don’t Lie,” proved through his research that mineral deficiencies are the number one cause of disease. Medical Studies have shown that the trace mineral element selenium plays a critical role in thyroid hormone metabolism. Foods rich in selenium include tuna, turkey, grass-fed beef, Brazil nuts, and sea moss.
- Glutathione: An antioxidant that supports thyroid health by reducing oxidative stress on thyroid cells. If glutathione levels are inadequate, cells will likely not correctly utilize glucose for energy, resulting in a downregulation of the thyroid gland.
- Vitamin B1 (Thiamine): Crucial for turning food into energy. Adequate levels help prevent symptoms like confusion, fatigue, heart problems, muscle weakness, and short-term memory loss.
- Vitamin B12: Helps repair damage caused by hypothyroidism and alleviates fatigue that thyroid disease can cause.
- Probiotics: Probiotic supplements contain helpful bacteria that support gastrointestinal health, which hypothyroidism can affect. This can potentially lead to conditions like small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) and chronic GI symptoms, such as diarrhea.
At Natural Max Health, we believe in treating the whole body rather than just addressing symptoms. To effectively manage hypothyroidism and other health issues, it’s essential to target the root causes. Many health problems stem from poor diets, resulting in mineral and vitamin deficiencies and mental imbalances like stress, anxiety, and depression. By focusing on these underlying factors, we aim to promote holistic healing and overall well-being.
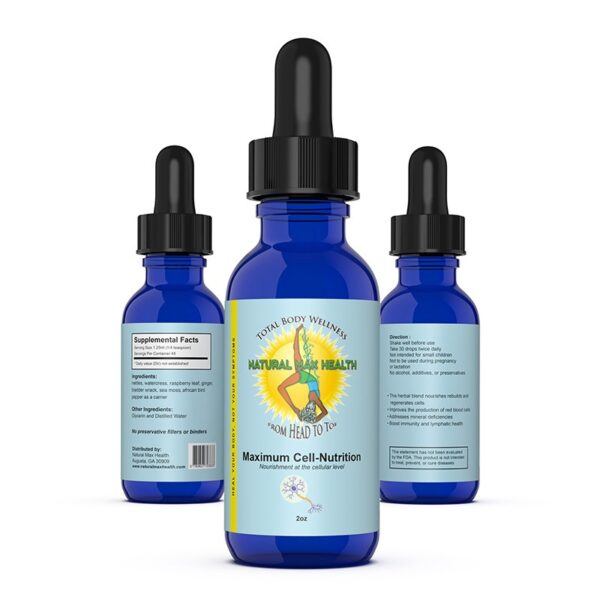
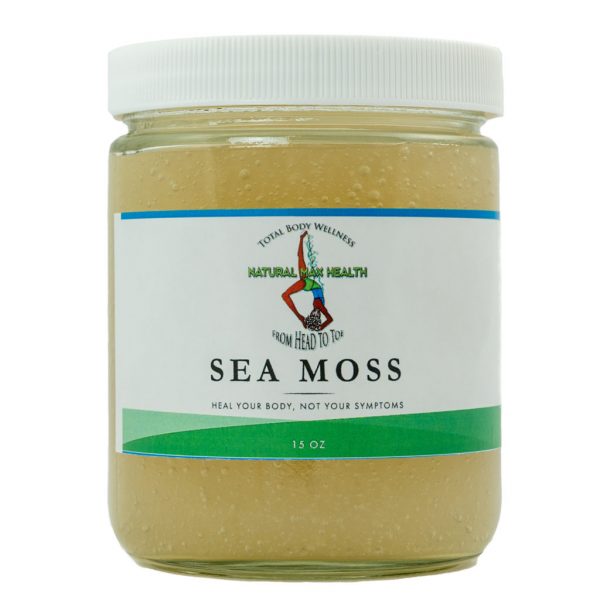
Therefore, depending on your diagnosed condition, taking supplements for deficiencies can benefit you. In the case of hypothyroidism, selenium deficiency is a significant factor because it plays such a vital role in thyroid hormone metabolism. Several of our products at Natural Max Health contain selenium, like our Maximum Cell Nutrition and Sea Moss, shown below:
Maximum Cell Nutrition
Nourish and Regenerate Your Body’s Cells Product Description: Maximum Cell Nutrition is our specially formulated blend of wildcrafted herbs, which provides the 102 minerals the human body needs daily to maintain a healthy state. It benefits your body at the cellular level.
9 in stock (can be backordered)
Sea Moss
Cleanse and Nourish Your Body at the Cellular Level Product Description: Sea moss or Irish moss is a sea vegetable that grows on rocks close to shore. Naturally rich in nutrients and minerals, it’s an excellent source of food to improve your daily nutrition. A Recognized Superfood Sea moss contains over 90% of the minerals the human body comprises and needs to maintain a healthy state to include: iodine, potassium, calcium, selenium, copper, beta carotene, folate, iron, sulfur, ash, manganese, and zinc. Also rich with antioxidants and amino acids, sea moss pulls toxins from the body to stimulate healthy digestion,…
Available on backorder
What Foods To Avoid, if Diagnosed With Hypothyroidism
Gluten-free diet: According to the National Foundation for Celiac Awareness, a significant number of people with thyroid disease also have celiac disease. Many individuals with hypothyroidism have reported feeling better after removing wheat and other foods containing gluten from their diets.
Sugar-free diet: Sugar and processed foods can increase inflammation in the body. Inflammation can slow the conversion of T4 to triiodothyronine or T3, which can make symptoms of thyroid disease worse. Removing or reducing sugar and processed foods from your diet can benefit your thyroid and overall health.
Avoid iodine-rich foods such as iodized salt, seaweed, and some seafood. Be careful with iodine supplements unless recommended by a doctor. High doses of iodine can interfere with the thyroid’s production of hormones, which can worsen an underactive thyroid.
Finally: Improve Your Lymphatic System for Overall Good Health
Never discount the importance of having a healthy lymphatic system when addressing any disease you may encounter. A healthy lymphatic system is essential for removing waste and harmful toxins from the body. To improve your lymphatic health:
- Stay active: Move your body! Regular physical activity helps maintain a healthy lymphatic system.
- Rebounding: Jumping on a mini-trampoline stimulates lymphatic circulation.
- Dry brushing: Gently brushing the skin helps move lymphatic fluid.
- Lymphatic massages: Professional massages can improve lymphatic drainage.
Takeaways
Living with hypothyroidism can be challenging, but with proper treatment and lifestyle changes, it is manageable. Natural remedies and dietary considerations can support conventional treatment methods, helping you lead healthier. Understanding your body’s needs and making informed choices can significantly improve your health and well-being.
The benefits of implementing natural remedies into your lifestyle far outweigh any disadvantages. Understanding how your body functions is essential to learning how to reverse or prevent illness. With some discipline and lifestyle changes, this disease can be manageable or even reversible. Your outcome depends on your willingness and drive to incorporate the suggested changes into your lifestyle.
If you found this article helpful, please share it with someone who might benefit. Until next time, take care of yourself, and happy healing!


